Texas insurance agency license: different types and licensing requirements
Texas insurance agency license: different types and licensing requirements | Insurance Business America
Guides
Texas insurance agency license: different types and licensing requirements
Getting a Texas insurance agency license is no simple feat. In this guide, find out the different licenses you need and how you can get them
All businesses venturing into insurance sales in Texas are required to obtain the proper licenses before they can legally operate. This is often the first and most important step that insurance entrepreneurs must take if they want to start their own agency. The process of getting a Texas insurance agency license, however, isn’t as straightforward as it seems.
Insurance Business sifted through all available information from the Texas Department of Insurance’s (TDI) website to help you sort things out. We will give you a primer on the different licenses you may need to start your own insurance agency, along with the licensing requirements.
If you’re planning on launching your own insurance sales business in the Lone Star State, this guide can prove handy. Read on and find out how you can secure your Texas insurance agency license.
Much like other states, you will need to get the right licenses to sell insurance products and services in Texas. The licensing requirements vary depending on the type of agency and insurance lines, but generally, TDI provides two main types of insurance agency licenses:
1. Resident insurance agency license
This type of license allows you to operate your insurance agency within state lines. It works just like the licenses insurance agents and brokers in Texas need to sell policies, but on a business level.
2. Non-resident insurance agency license
You need this type of license if your business is based out of state, and you plan on serving clients in Texas. This comes with corresponding fees and requirements.
Certain states have reciprocity agreements with Texas. These allow them and their agents to apply for licenses without the need to take the state licensure exam.
Insurance business owners can choose different lines of authority to specialize in. You will need to have the necessary license for each insurance line to sell policies.
TDI groups insurance agencies into different categories, with each needing to get the proper licenses to operate. These are:
County mutuals
The Texas Insurance Code defines a county mutual as an insurance company that “qualifies to write casualty lines for statewide operation.” These businesses are only allowed to assume risks that are worth less than 5% of their total assets unless they reinsure the excess amount of risk.
While county mutuals are required to comply with rate and form regulations, they are exempt from most insurance laws. These include the Texas Auto Insurance Plan Association (TAIPA) rules.
There are 23 county mutuals across Texas. State insurance laws no longer allow the formation of new county mutuals.
Funeral pre-arrangement life insurance agencies
This type of life insurance agency writes life insurance policies and fixed annuity contracts designed to deliver funeral services and merchandise. These businesses are regulated by the Texas Department of Banking (TDB) under Chapter 154 of the Finance Code or Prepaid Funeral Services.
General lines insurance agencies – life, accident, health & HMO
These agencies specialize in selling life, accident, and health (LA&H) insurance policies. They also offer health maintenance organization (HMO) services. These insurance agencies can also sell annuities and Medicare products, but they must meet additional requirements.
General lines insurance agencies – property and casualty
These insurance agencies sell policies under the property and casualty (P&C) line. This includes auto, home, commercial, liability, pet, and cyber insurance.
Life insurance agencies
These businesses specialize in selling life insurance policies. If you want to start a career in the field, our guide on how to get a life insurance license is a must-read.
Life insurance agencies for policies not exceeding $25,000
These entities are authorized to sell life insurance policies worth $25,000 or less. Agents who specialize in this limited line are not required to hold a life insurance license if they plan to sell this type of coverage exclusively.
Limited lines insurance agencies
A limited lines insurance agency sells policies other than the six general lines defined by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) listed below.
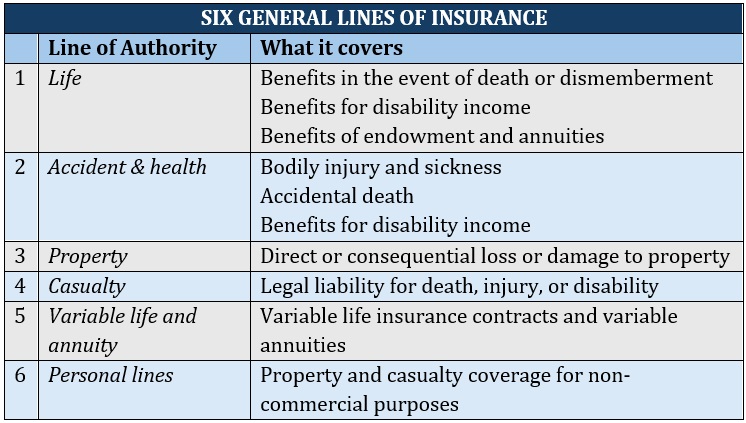
Some examples of limited lines include credit insurance, crop insurance, farm insurance, and travel insurance. Because such policies are “limited,” insurance agencies and agents are often able to sell them without the need for additional licensing.
Managing general agents (MGA)
MGAs are agencies contracted by insurance and reinsurance companies to perform certain tasks. These include claims handling, underwriting, binding, policy administration and distribution. These firms enable insurers to focus on the products and services they provide.
Personal lines insurance agencies
Personal lines agencies offer policies that combine LA&H and P&C elements. Agents offering such products may be required to get licenses on both general lines.
Surplus lines insurance agencies
These insurance agencies offer policies for highly complex risks that traditional insurers aren’t willing to cover. Agencies often access such products from surplus lines specialists, also referred to as non-admitted insurers.
Title insurance agencies
Title insurance is a type of policy that protects homebuyers and lenders from financial losses stemming from issues with the ownership title of the property. Title insurance agencies specialize in this form of coverage.
All businesses involved in selling insurance in Texas are required to apply for the necessary licenses on the Sircon or the National Insurance Producer Registry (NIPR) websites.
The table below contains a step-by-step tutorial from TDI on how you can apply for the different Texas insurance agency license online.
During application, you will be asked to provide the following details:
all executive officers, directors, or partners who handle your insurance agency’s operations in Texas
all individuals and entities in control of your insurance agency’s operations
You will also be asked to name at least one officer or active partner who must have a license with the same line of authority. In some states, these representatives are called a “designated responsible licensed producer” or DRLP. A DRLP is a licensed insurance professional in charge of making sure that your insurance agency complies with the laws of the state you’re operating in.
The application fee is $50, regardless of the type of Texas insurance agency license you’re applying for.
Running an entire agency can be overwhelming for some people. If you feel like a career as an individual agent or adjuster suits you better, this guide on how to get a Texas insurance license can help.
When starting an insurance agency in Texas, you must be aware of the different licenses, permits, registrations, and certifications you may need apart from insurance licenses. Here are some of them:
General business license: Most counties and cities in Texas don’t require a general business license or permit for local enterprises. Each jurisdiction, however, has its own licensing requirements, which vary depending on the business. This Texas Business Licenses & Permits Guide from the Business Permit Office can help you sort out what business permits and licenses you need for your insurance agency.
State registration: All insurance businesses are required to register as a “resident business entity” through the TDI.
Tax identification number: If your insurance agency operates as a partnership or corporation, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires you to use your federal employer identification number (FEIN) when filing taxes. If the business is structured as a sole proprietorship or single-member LLC, you may use your Social Security number.
Texas law requires any business or individual involved in the sale of insurance policies to secure the right licenses. Selling insurance without the necessary licenses can result in a felony charge. Individuals and entities can also face heavy financial and legal penalties, including:
monetary fines
blocked commissions
suspension or revocation of insurance and business licenses
The state insurance department may also issue cease-and-desist orders to prevent your insurance agency from doing business. If this happens, you may be required to pay any unsettled insurance claims.
There are several ways for an insurance agency to make money. These include one or a combination of the following:
1. Commissions
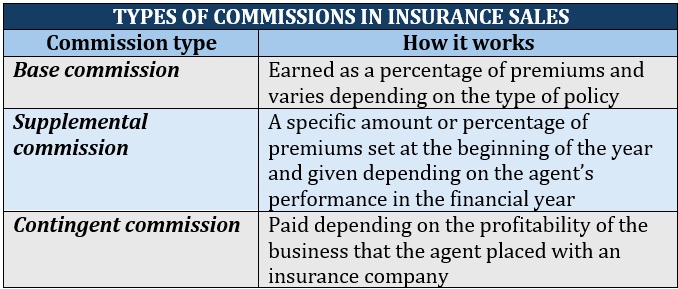
Insurance agencies typically generate profits through base commissions, which are influenced by the type and quantity of insurance policies sold. Whether the policies are new or renewals also affect how much commission the agency receives.
Some insurers also offer insurance agencies supplemental and contingent commissions. These are intended as incentives for agencies and agents who help them achieve certain business targets.
Here’s a summary of how these types of commissions differ.
2. Advisory or consulting services
Many insurance agencies offer consultative and advisory services to help clients make informed decisions about their insurance purchases. These services come with corresponding fees. These fees are mostly state regulated just like insurance commissions.
3. Bonuses or profit sharing
Some insurance companies implement profit-sharing programs for their partner agencies. Insurance agencies that reach certain revenue targets receive a percentage of either written or earned premiums as a bonus.
The continued growth of the insurance industry presents a massive opportunity for entrepreneurs who want to venture into the insurance business. Insurance products and services will always be in high demand as long as people need financial protection.
Just like any type of business, operating your own Texas insurance agency requires careful planning and preparation. If you’re an aspiring insurance business owner but not quite sure where to begin, this guide on how to start an insurance company can provide useful tips.
Do you think starting an insurance agency in Texas is worth it? Did you find our guide on Texas insurance agency license helpful? Share your comments below.
Keep up with the latest news and events
Join our mailing list, it’s free!






