What is an underwriting agency?

What is an underwriting agency? | Insurance Business Australia
Insurance News
What is an underwriting agency?
An insurance underwriter plays an integral part in the insurance process. Find out what exactly these professionals do in this guide
Insurance News
By
Mark Rosanes
Insurance underwriters play an essential role in protecting insurers from unnecessary financial losses. That’s what makes these industry professionals an integral part of every insurance company. But what does an insurance underwriter do exactly?
In this article, Insurance Business explains the important contributions these professionals make in the whole insurance process. We will give you a walkthrough of their duties and responsibilities, as well as the skills needed to be successful. We will also discuss how much they earn and how the role differs from other insurance jobs.
If you’re considering an insurance career or simply want to understand what an insurance underwriter is, you’ve come to the right place. Get to know more about these industry professionals in this guide.
An underwriting agency is a specialised type of insurance agent or broker that has been granted underwriting authority by an insurer. It can also administer programs and negotiate contracts for an insurer.
An underwriting agency’s functions can include binding coverage, underwriting, pricing, settling claims, and appointing retail agents in a certain region. All these tasks are typically carried out by insurers.
At its core, the underwriting agency manages all or part of the insurance business of an insurer. It also acts as an insurance agent or broker for the insurer, while working as the intermediary between insurers and agents, and the insureds.
How do underwriting agencies fit into the distribution channel?
Wholesale insurance brokers act as an intermediary between a retail broker and an insurer, and work with insurers to attain specialised coverage for clients while having no contact with the insured.
An underwriting agency is one type of wholesale broker. It operates on the insurer’s behalf while also working closely with clients to attend to their needs. The other type of wholesaler is a surplus lines broker who works with a retail agent and an insurer to obtain coverage for the insured. What makes underwriting agencies unique is their binding authority from the insurer.
Underwriting agencies deliver and service an insurer’s product to both insurance agencies and clients. They can work with several insurers to formulate a specific mix of products to deliver to agents and brokers or directly to insureds.
An insurance underwriter determines whether an insurer can provide coverage to a specific client by assessing the potential risks of insuring them. Underwriters often work closely with other industry professionals, including risk managers, actuaries, and insurance agents and brokers. Their goal is to come up with ways insurance companies can strike a balance between offering affordable premiums and maintaining profitability.
Most insurance underwriters in Australia specialise in a single line, although there are some who handle a range of expertise. Some of the most common specialties include:
Insurance underwriter: Areas of specialty
Property & casualty insurance
An umbrella term given to a range of policies that cover personal belongings (property) and liability (casualty); includes home, car, pet, travel, and business insurance
Business insurance
Policies that cover commercial risks
Life insurance
Underwriters assess premiums for death benefits; includes disability and income protection insurance
Health insurance
Private health insurance plans
Reinsurance
Policies purchased from another insurer (reinsurer) that allow insurance companies to split the risks.
The main role of an insurance underwriter is to evaluate a potential client’s risk exposure to find out if it’s financially feasible for the insurer to provide coverage. However, the scope of their jobs goes beyond this.
Analysing information that clients disclose on their insurance applications
Determining the likelihood that a potential client will file a claim
Screening applicants based on set criteria, which vary for each insurance line
Obtaining additional information about clients; this may involve contacting other professionals, including field representatives and medical personnel
Defining the terms and conditions of coverage, along with appropriate premiums
Ensuring that the rates are competitive, and accounts remain profitable
Using technology when determining the risks of insuring clients
Reviewing recommendations of these automated platforms
Reassessing the risks when policies come up for renewal
Organising records of underwriting decisions and underwritten policies
Most underwriters work for insurance companies, often acting as intermediaries between the insurer and the insurance agents and brokers. However, insurance underwriters can also find employment in banks, credit agencies, life assurance firms, and other financial institutions.
Most insurance underwriting jobs are office-based and have a standard full-time work week. Part-time and flexible work options are also available.
Most insurance companies prefer candidates with a bachelor’s degree to fill insurance underwriter vacancies. Insurers, however, may also consider candidates with adequate work experience, especially for entry-level roles, even if they only have a vocational certificate. Insurance-related certifications can likewise boost a candidate’s employment chances.
Here are some common requirements insurance companies in Australia set when screening potential insurance underwriters.
Insurance underwriter education
Although not always required, a bachelor’s degree can increase your chances of being hired. Some relevant degrees that you may want to consider if you plan on pursuing a career as an underwriter include:
Accounting
Actuarial science
Business administration
Computer science
Economics
Finance
Information technology
Mathematics
Risk management
Statistics
You can also take insurance underwriting courses and other related programs in accredited educational institutions. Some universities also offer master’s degrees in insurance risk management, which can open opportunities for career advancement.
Insurance underwriter professional training
Entry-level staff often work under the guidance of a senior underwriter for a certain period until they can do their jobs with minimal supervision. Some insurance companies also provide training programs for new hires to help them perform their roles effectively.
Insurance underwriter certifications
As an insurance underwriter, you’re expected to obtain different certifications to progress your career. These are especially important if you’re targeting a senior underwriter or underwriter manager roles. Each specialisation also has its range of underwriting certifications that can keep you abreast of new products, regulatory and legislative changes, and the latest industry innovations.
Here are some examples of certifications that you can take to help advance your insurance underwriting career:
ANZIIF Executive Certificate in General Insurance Underwriting
The Australian and New Zealand Institute of Insurance and Finance (ANZIIF), also referred to as the Institute, offers an Executive Certificate in General Insurance Underwriting. This is designed for insurance professionals with at least four years of industry experience who are specialising or want to specialise in underwriting.
Students must complete 80 credit points, half of which are required for any general insurance underwriting specialisation. The rest are elective units.
Once completed, students earn a certificate and are eligible to move up to as Senior Associate Certified Insurance Professional (CIP) member.
FNS41515 Certificate IV in Life Insurance – Underwriting Stream
The FNS41515 Certificate IV in Life Insurance training course is designed for industry professionals who are already working or plan on pursuing a career in life insurance.
The underwriting stream is centred on underwriting complex medical and non-medical risks and the use of specialist insurance terminology. It also includes courses on legislation, products and services, claims processing, and customer service.
FNS40510 Certificate IV in Personal Injury Management (Underwriting)
The underwriting stream of the FNS40510 Certificate IV in Personal Injury Management is designed for professionals working or planning a career in personal injury management. The course consists of four core units and nine elective units. It is suitable for roles within the workplace injury and CTP insurance fields.
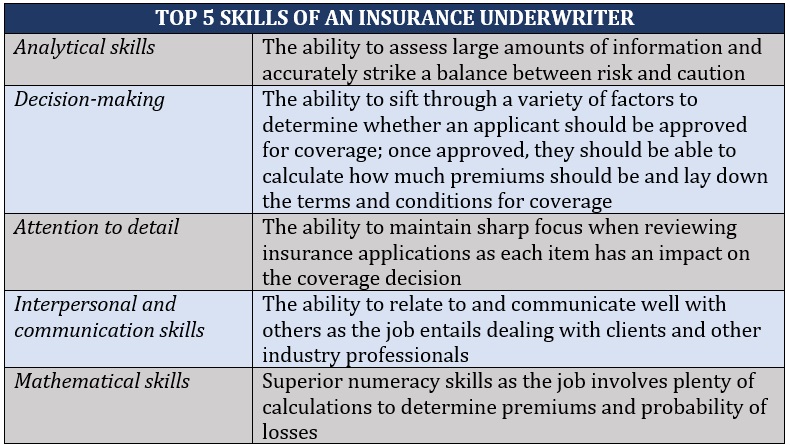
What skills do you need to become an insurance underwriter?
Insurance underwriters must possess a combination of hard and soft skills that can allow them to evaluate risks objectively and work harmoniously with other industry professionals. Here are the five most important skills that insurance underwriters should have to thrive in their careers.
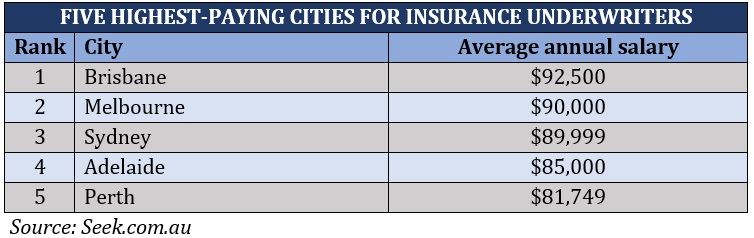
Insurance underwriter salaries in Australia start at $68,000 and can exceed $100,000, depending on the role and level of experience. The average annual salary of an entry-level professional is about $74,800 while senior management salaries can reach $172,000. These figures are based on the employment websites Insurance Business checked.
This recruitment site also provided the five highest-paying cities for insurance underwriters, which are:
Is insurance underwriting a stressful job?
Insurance underwriting can be a stressful job. Underwriters are under constant pressure to attract and retain clients while helping insurers maintain profitability.
These goals often come into conflict with each other, especially in a highly competitive market. But with the right mix of technical ability and soft skills, insurance underwriters can excel in their role.
What is the difference between an insurance underwriter and an insurance agent/broker?
Insurance underwriters, agents, and brokers all play important roles in helping clients access the right types of coverage. These industry professionals, however, perform vastly different tasks.
As discussed above, an insurance underwriter works mostly for an insurance company. These professionals assess the risks potential clients pose and decide if they can be approved for coverage. Underwriters use a range of metrics to calculate premium pricing and the terms and conditions of coverage, while bearing in mind the insurer’s ability to maintain profit.
Insurance agents and brokers, meanwhile, act as intermediaries between the buyers and the insurance companies. Their goal is to assist individuals, families, and businesses in finding policies that cater to their unique needs. They can work independently or as part of an insurance agency or a brokerage firm.
So, while insurance underwriters put the interest of the insurance company first, insurance agents and brokers serve the customers. These sales professionals help clients find the coverage that suits their needs and budget.
Why is insurance underwriting important?
Underwriting is an important part of the insurance scheme of things. It allows insurers to maintain a healthy loss ratio, which represents the amount of losses incurred versus premiums earned. Along with good investments, sound underwriting is a key driver of an insurance company’s financial performance.
Bad underwriting decisions can push insurance companies to pay more in claims, impacting their profitability. By implementing solid underwriting strategies and investing in staff training, insurers can lessen the unpredictability of their underwriting results.
How do underwriting agencies benefit insurers and agents?
Working with underwriting agencies is beneficial to insurers because they possess expertise that insurers may not have in their head or regional offices and can be costly to develop in-house. Working with an underwriting agency, companies can pass time-consuming and complicated tasks to an outside entity that already has the knowledge to address them.
Underwriting agencies tend to deal in lines of coverage such as professional liability, employee benefits or surplus lines where specialised expertise is needed to underwrite policies. However, they can also be active in any line of insurance and work with all types of insurers.
If insurers want to explore a specialty line of business but don’t want to take on the risks or uncertainty of doing so, they can turn to an underwriting agency to offer up that expertise. They can also give underwriting agencies the authority to underwrite and issue specialty policies because they are already familiar with the risks.
Underwriting agencies can also write business in geographically isolated areas where insurers don’t want to open an office. A small town or rural region, for instance, might not warrant the opening of a branch for an insurer. But working with an underwriting agency in that area provides the company with access to new customers without spending money on staff or rent.
Similar to insurers, agents can get expertise about a particular product or more competitive pricing by working with an underwriting agency. They can likewise gain entry to markets and insurers that could be difficult to access on their own. And because of the often-smaller size of the underwriting agency business, there are fewer barriers to communication for a broker.
Underwriting agencies also bring technology to the table, such as online platforms that integrate with wholesale channels or products that speed up the quoting process. This can help independent agents provide better services to their clients.
Agents can earn higher commissions by working with an underwriting agency that has a diverse network of insurers. This also allows agents to review the commission structure and have the option to sell insurers’ products that offer the best rates.
In other markets, underwriting agencies are known as managing general agencies (MGAs) or managing general underwriters (MGUs). Many MGA models were created during the 1990s and 2000s, though the role of the wholesale broker, a category that MGAs fall into, dates back to the 19th century. Associations that represent MGAs or underwriting agencies in specific regions today include:
The UK’s Managing General Agents’ Association (MGAA), which was formed in 2011
The American Association of Managing General Agents (AAMGA), which was established in 1926 and has since merged with the National Association of Professional Surplus Lines Offices (NAPSLO) to form the Wholesale & Specialty Insurance Association (WSIA)
The Canadian Managing General Agents (CAMGA), a relatively new association formed in 2017
Australia has the Underwriting Agencies Council (UAC), which is based in Sydney and formed in 1998. According to the UAC, its 134 members account for more than $6 billion of premiums spent by Australian businesses and consumers annually.
In the UK, the term “MGA” has been adopted by the market to refer to what was once known as a “coverholder.” Today, more than 300 MGAs underwrite over 10% of the UK’s £47 billion general insurance market premiums, according to the MGAA.
Worldwide, MGAs fall into one of the fastest-growing segments of the insurance industry. Global investment firm Conning reported that MGA and program market growth continue to outpace the growth of the property and casualty market. The MGA direct premium growth of 27% is higher than the previous year compared to the 10.5% seen in P&C market growth. The analysis also showed that 21 of the top 25 P&C insurers have relationships with MGAs.
What is the role of an underwriting agency today?
With technology bridging the gap between insurers and clients, some insurers are moving away from relying on MGAs or underwriting agencies. The situation has thrown the identity and future of these organisations into question.
“By virtue, MGUs and MGAs, program administrators, are the middlemen,” explains Rekha Skantharaja, president and CEO of Tangram Insurance Services. “How can we make sure we stay ahead, make sure that we take advantage, and make sure that we continue to be relevant and meaningful to a broker, to an insurer, to a tech investor, to say, this entity still belongs in the middle of all of this?”
However, an underwriting agency is a natural outlet for technological solutions to plug into because of its established distribution channels. These agencies can also react to market changes quicker than typical insurance companies because they are smaller businesses that are acting on behalf of larger insurers.
“We can bring programs to the market faster,” explains Skantharaja. “We can get out to more brokers because they can get on our platform. We can reduce our expenses as an MGU because now we’re automating a lot of things.” She adds that there’s “an unprecedented opportunity” for partnerships between technology vendors and MGUs.
During hard market periods, underwriting agencies can be used by insurers to decrease costs and increase profitability.
The underwriting agency model is also flexible. Following the 2008 financial crisis, Ironshore, a Liberty Mutual company, established its managing general underwriting agency as its commercial clients were facing heightened risk. This is because the viability of some insurers that offered high coverage limits across many lines of business for major companies was uncertain.
Brokers were also under pressure to find alternative coverage solutions. The Ironshore model involved underwriting as well as claims management. The latter made it unique to a traditional agency, which can have limited authority on claims management and payments.
Our Best in Insurance Special Reports page is the place to go if you want to find the best underwriters in Australia. The insurance professionals and underwriting agencies featured in these special reports were handpicked by their peers and vetted by our panel of experts as reliable and dependable market leaders.
By choosing to partner with these individuals and companies, you can be sure that you’re dealing with professionals who can provide you with the right coverage when you need it.
What do you think of the role an insurance underwriter plays in the industry? Feel free to comment below.
Related Stories
Keep up with the latest news and events
Join our mailing list, it’s free!






