20% of US GDP to be spent on health care
That is the conclusion from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services National Health Expenditure Projections. The paper–published in Health Affairs—summarizes the spending changes as follows:
National health expenditures are projected to grow 5.4 percent, on average, over the course of 2022–31 and to account for roughly 20 percent of the economy by the end of that period. The insured share of the population is anticipated to exceed 92 percent through 2023, in part as a result of record-high Medicaid enrollment, and then decline toward 90 percent as coverage requirements related to the COVID-19 public health emergency expire. The prescription drug provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 are anticipated to lower out-of-pocket spending for Medicare Part D enrollees beginning in 2024 and to result in savings to Medicare beginning in 2031.
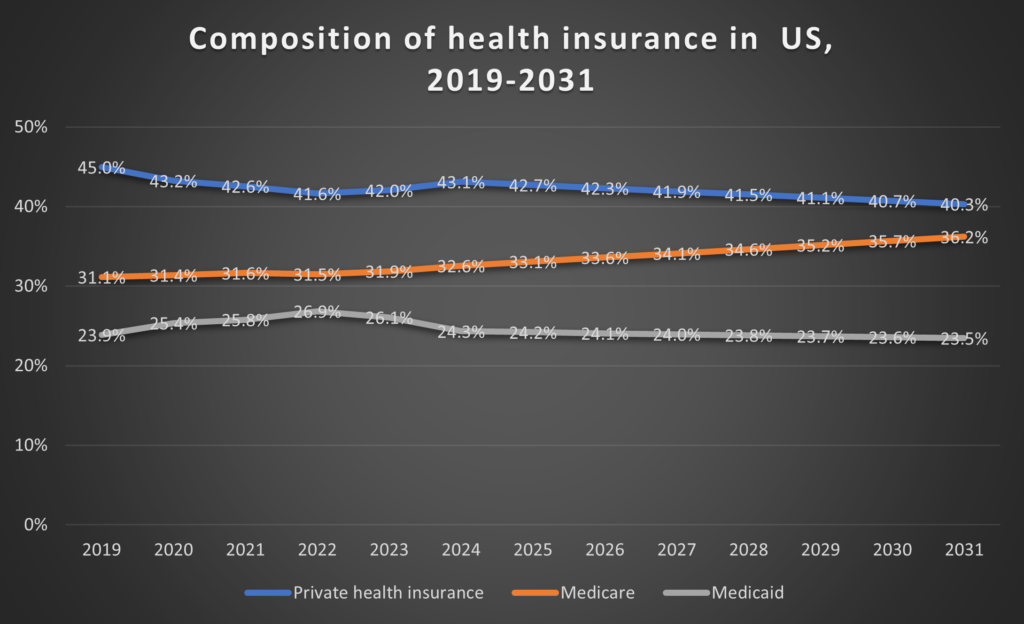
As the population ages, we see that Medicare will make up a growing percentage of the insured individuals in the US. Note that the figure below only includes Medicare, Medicaid and Private insurance and linearly interpolates these rates between 2024 and 2031.
Regarding the impact of the Inflation Reduction Act, the authors write:
One provision from the Inflation Reduction Act that is expected to put upward pressure on Medicare spending growth is the anticipated outlays that the program will pay to cover the cap on Part D out-of-pocket spending at $2,000 per year, which takes effect in 2025. However, Medicare is expected to experience slower growth in spending toward the final years of the projection period, reflecting the full effect of the Inflation Reduction Act’s provisions that allow the program to negotiate prices for certain Part D drugs and that link drug price increases to the CPI.
The full article is available here.







